Consider the Experiment of Tossing a Coin Three Times
Of a statistical experiment. So not surprisingly if we.
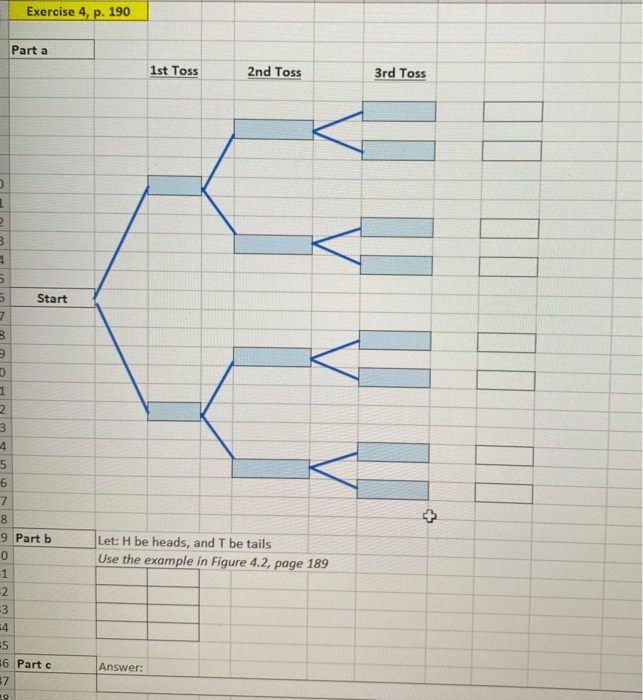
Solved 4 Consider The Experiment Of Tossing A Coin Three Chegg Com
So an event for an experiment is the collection of some outcomes of the experiment.
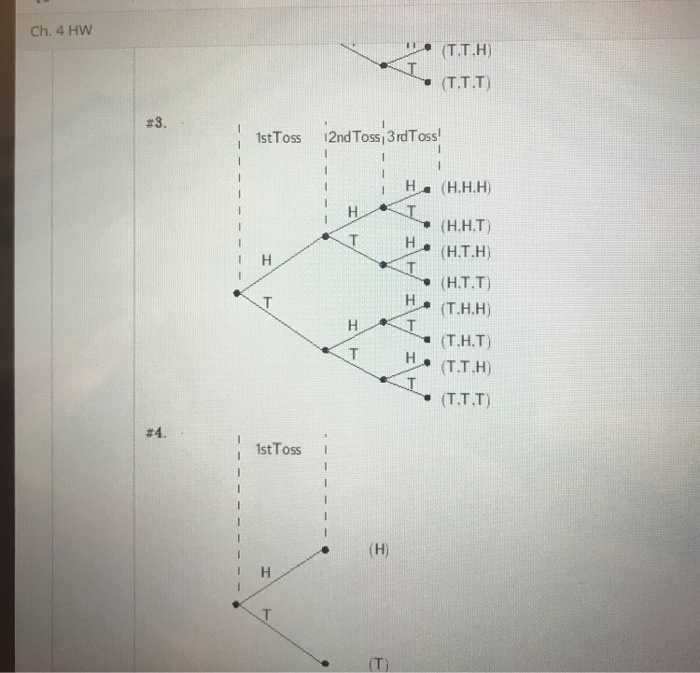
. If a coin is tossed three times the likelihood of obtaining three heads in a row is a. An experiment consists of first rolling a die and then tossing a coin. Sometimes it is also known as the discrete density function.
And what is the variance of this distribution. In probability and statistics a probability mass function is a function that gives the probability that a discrete random variable is exactly equal to some value. So can you now tell what the events are in Activity 4.
5 if it a tail. The set of all the possible outcomes is called the sample space of the experiment and is usually denoted by S. 5 is you get head and will lose Rs.
Consider the random experi-ment of tossing a coin three times and observing the re-sult a Head or a Tail for each toss. If the reviewers disagree the editor sends it to a third reviewer and does whatever he or she advises. An experiment consists of tossing 4 coins successively.
If our experiment was to throw the die for getting an even number then the event would consist of three outcomes namely 2 4 and 6. A coin is tossed four times. 2 boys and 2 girls are in Room X and 1 boy and 3 girls in Room Y.
The sample space is S fHTg. List the sample space. Let X number of times the coin comes up heads.
For instance in an experiment where we flip a coin ten times we may care about both Xomega the number of heads that come up as well as Yomega the length of the longest run of consecutive heads. We notice you are outside the United Kingdom. Suppose that the coin is flipped 3 times.
Each outcome in a sample space is called a sample point. You will earn Rs. At the moment we only ship our products to addresses in the UK.
Any subset E of the sample space S is called an event. In Class X you will study a more formal definition of an event. The number of sample points in this experiment.
E fHgis an event. The 8 possible elementary events and the corresponding values for X are. Here are some examples.
31 Joint and marginal distributions. The definition of the mutually exclusive event is expanded to two or more events. Consider the selection and classification of the cards as odd or even as an experiment.
Consider the experiment in which a person flips a loaded coin such that head is three times more likely to appears than tail. A die is thrown two times. This pastichewhich is not far from systems I have seen usedis little better than tossing a coin because the level of agreement between reviewers on whether a paper should be published is little better than youd expect by chance.
Example 2 Tossing a die. Consider our earlier coin tossing experiment. Let A be the event of a perfect square number then A 14.
In this section we consider the setting of two random variables. The random variable of interest is. The sample space is S.
A coin is tossed three times. Let A be the event that either a three or a four is rolled first followed by landing a head on the coin toss. The probability mass function is often the primary means of defining a discrete probability distribution and such functions exist for either scalar or multivariate.
A Construct a table that shows the values of the ran-dom variable X for each possible outcome of the random experiment. Consider the situation we throw a dice. A coin is tossed and then a die is rolled only in case a head is shown on the coin.
Let X denote the total number of heads obtained in the three tosses of the coin. Consider the random experiment of tossing a coin 20 times. For example there are only two outcomes for tossing a coin and the sample space is S fheads tailsg.
A List all the outcomes of. If we toss a coin three times how many times do we expect it to come up heads. X px xpx x - µx5 x - µx5px 0 18 0 225 2258 1 38 38 025 0758 2 38 68 025 0758 3 18 38 225 2258 Σ xpx 15.
Once we get these three values then we could look up Chi-Squared table because 072 is less than 384 we can not reject null hypothesis so we can make the conclusion that the coin is fair. The gamblers fallacy also known as the Monte Carlo fallacy or the fallacy of the maturity of chances is the incorrect belief that if a particular event occurs more frequently than normal during the past it is less likely to happen in the future or vice versa when it has otherwise been established that the probability of such events does not depend on what has happened in the. It is also called an element or a member of the sample space.
PDF On Nov 26 2020 Pasquale Bosso and others published Experimental test of fair three-sided coins Find read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate. If we toss a coin three times then the sample space is. In the experiment of picking 3 balls from a bag containing 10 balls 4 of which are red and 6 blue we can consider picking each ball to be an event and therefore say that there are 3 trials in the experiment.
The probability of success is constant from trial to trial 4. Here we see that the value of getting head for the coin tossed for 20 times is anything from zero to twenty. Whenever an outcome agrees with the condition given in the event we say that event has appeared.
You and your friend are all set to see who will win the game by earning more money. Consider a random experiment. The experiment is a sequence of independent trials where each trial can result in a success S or a failure F 3.
Two cards are drawn. How many sample points are. A coin is tossed and a die is thrown.
An event is an outcome or the union of an outcome of an experiment. Elementary event Value of X TTT 0 TTH 1 THT 1 HTT 1 THH 2 HTH 2 HHT 2 HHH 3 Therefore the probability distribution for the number of heads occurring in three coin. The experiment continues trials are performed until a total of r successes have been observed so the of trials is not fixed 5.
Consider the simple experiment of tossing a coin three times. In the experiment of tossing 4 coins we may consider tossing each coin as a trial and therefore say that there are 4 trials in the experiment. Example 1 Tossing a coin.
Because of this we do not allow traffic to our website from outside the UK so unfortunately you will.
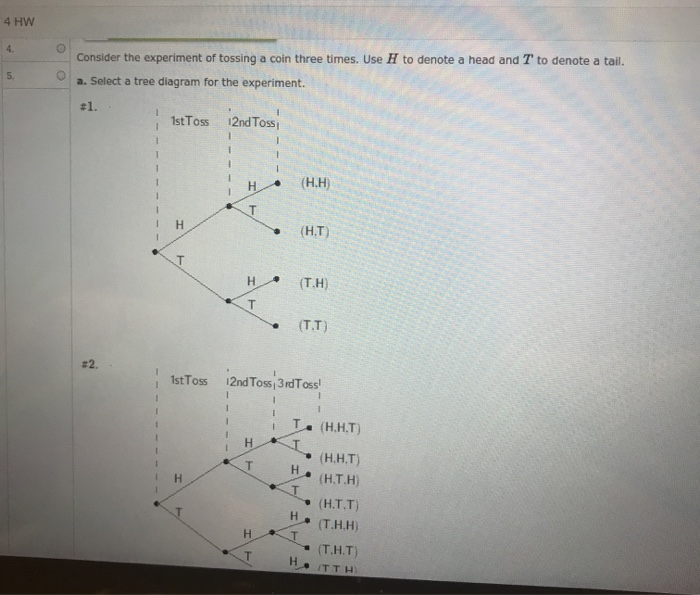
Solved Consider The Experiment Of Tossing A Coin 3 Times Chegg Com

Solved Consider The Experiment Of Tossing A Coin 3 Times Chegg Com
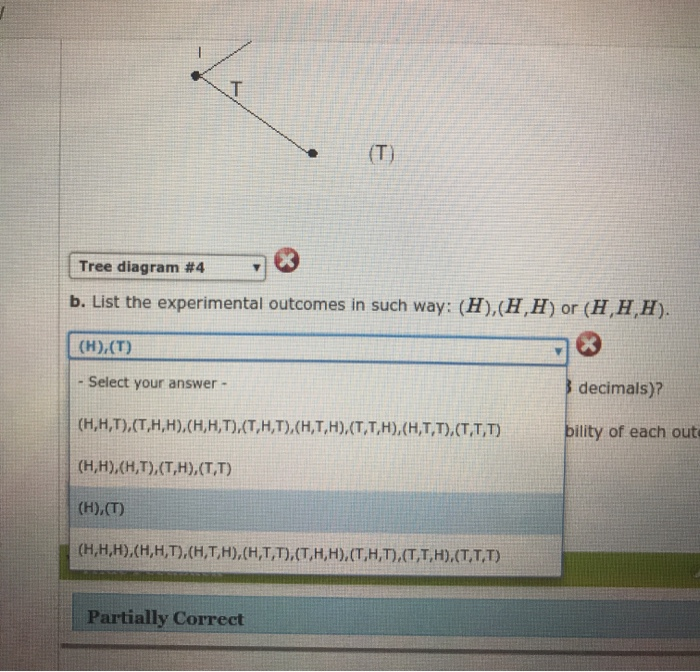
Solved Consider The Experiment Of Tossing A Coin 3 Times Chegg Com
No comments for "Consider the Experiment of Tossing a Coin Three Times"
Post a Comment